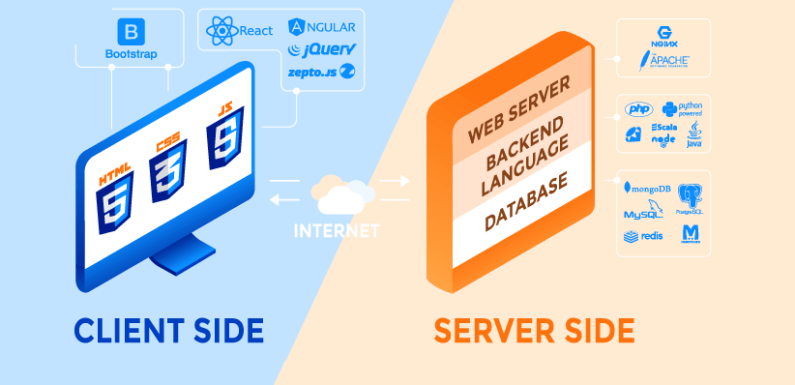
The web works according to a really simple principle: the web servers host the contents and the clients request them by HTTP or FTP, understanding by clients the browsers (Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome) installed in the user’s system, where they are executed. On the contrary, web servers, such as Apache or NGINX, are part of web development projects, are installed and run in this environment and allow customers access to content.
Static contents, such as classic HTML elements or images, are simply sent to the browser and visualized there, dynamic contents, such as a Wiki, a drop-down menu or any type of web application only work through scripts, which they must be executed and interpreted with the corresponding web programming language on the server side or on the client side. This is why it differs fundamentally between server-side programming languages and client-side languages.
What is server-side programming?
Server-side programming comes into play in the development of web pages with dynamic elements and web applications. This web development technology is based on the use of scripts executed by the web server, with the help of the appropriate programming language, when a client requests the content. A frequent task of scripts is to extract the data that is needed from a database and integrate it into the web project. Although the user accesses the project through HTML pages, the source code of the scripts remains hidden.
Also read: The Best Programming Languages for Developing Websites
The use of these server-side scripts presupposes that the client will continue to send requests to the web server to deliver new and modified information to the user. This, on the one hand, entails a heavy load on the server’s capacity, with the consequent influence on its response time and, on the other, it makes a connection to the server essential to be able to access the page.
In the early days of the network of networks, the programming of the server side was reduced almost exclusively to the development of programs in C, Perl and command line languages (CMD, PowerShell). These applications were executed and interpreted by the server operating system and the result could be transmitted from the web server to the browser that had made the request through a common gateway interface (Common Gateway Interface, CGI).
Nowadays, many web servers can execute the scripts directly, for example, with the help of modules. The server-side programming language most used today is PHP, published in 1995 and very similar to C and Perl.
The programming of the client-side
Client-side programming languages are also used to carry out projects with dynamic content, but unlike server-side languages, it is not the server that executes and processes the scripts, but the requesting client. For this purpose, the scripts are included in the HTML or XHTML document or written to a separate file that is linked to the main document.
When a user requests a web page or a web application with a script of this type, the web server sends the HTML document and the script to the browser, who executes it and presents the final result. Likewise, the client-side scripts contain specific instructions for the web browser on how to react to certain actions carried out by the user, such as a click on a specific button. Often, the client has to establish another contact with the web server for this.
Also read: 12 Reasons For Opting PHP For Your Next Web App Development Project
When running in the browser, the user can see the source code, unlike what happens with server-side scripts. In return, the interpretation of the scripts is based on the assumption that the web browser understands the corresponding web programming language. As pop-up windows and web tracking tools are also based on client-side language and these scripts influence loading times, there are several very popular browser extensions that block these scripts.
The most significant client-side language is JavaScript, developed by Netscape Brendan Eich (Netscape Communications Corporation), Software Company responsible for the creation of Mozilla Netscape’s predecessor browser, and published in 1995 along with the previous version of the Navigator 2.0 browser, even with the name of LiveScript.
Its use spread rapidly, soon becoming the universal web programming language of all relevant web browsers and even in the standard language of video playback on the Internet for many years as an essential component of Shockwave Flash (SWF), the video player of Adobe.However, due to vulnerabilities and more modern technologies such as HTML5, those videos and animations so widespread find less and less application. In the early days of the web, Microsoft Silverlight and the Java Applets were also very popular.
In theory, any web programming language could be used to program the client side, although this would imply that the developers of all the most important browsers should agree to support them. However, there are also alternative solutions that allow writing from the client side with other web programming languages. This is the case of transcompilers or transpilers such as CoffeeScript or TypeScript, which interpret the code and execute it as JavaScript.
Schedule with server-side or client-side languages?
The place where scripts are executed has a great influence on the structure of web projects. The more scripts are transferred to the scope of responsibility of the browser, the lighter the page or the web application for the server and, although this means a significant decongestion for the server, it can bring a worse performance for the user.
Also read: What Is Blockchain? How Blockchain Impacts Mobile Application Development
In addition, developers have to face a high degree of complexity if they bet exclusively on a client-side language like JavaScript since in this case, they have to recreate many mechanisms of more powerful frameworks such as ASP.NET MVC. And that’s not to mention that, when using client-side languages, the browser is expected to support the language used with all its functions and that the user does not use blocking extensions.
Consequently, in order not to overload one side or the other, it would be ideal to opt for a good combination of server-side and client-side languages and ensure reasonable loading times with additional measures such as static content caching and application. Of modern technologies such as AJAX, an acronym for “Asynchronous JavaScript and XML” (asynchronous JavaScript and XML). This concept is used in website development Brentford to transfer data asynchronously between client and server, which means that the web server can react to requests from the client side almost in real time and exchange information with the browser without having to load the page completely.

